Block&Inline
Understanding the HTML <div> Tag: Block-Level and Inline Elements
The HTML <div> tag is one of the most commonly used elements in web development. It is a block-level element that is primarily used for grouping and organizing content on a webpage. Understanding how to use the <div> tag effectively, along with the difference between block-level and inline elements, is essential for structuring and styling web content.
Key Points to Cover:
-
What is the
<div>Tag?:- Define the
<div>tag as a block-level element that is used to group and wrap other HTML elements. - Explain that the
<div>tag itself doesn’t affect the content it contains, but it can be styled with CSS to control layout, spacing, and appearance.
- Define the
-
Block-Level vs. Inline Elements:
-
Block-Level Elements:
- Block-level elements, like
<div>, start on a new line and take up the full width available. - Common block-level elements include
<p>,<h1> - <h6>,<ul>,<ol>, and<div>. - Block-level elements can contain other block-level elements or inline elements.
- Example:
<div>
<p>This is a paragraph inside a div.</p>
</div>
- Block-level elements, like
-
Inline Elements:
- Inline elements, such as
<span>, do not start on a new line and only take up as much width as necessary. - Inline elements are typically used for styling small pieces of content within a block-level element, like text within a paragraph.
- Common inline elements include
<a>,<span>,<em>,<strong>, and<img>. - Example:
<p>This is a <span style="color: red;">red</span> word in a paragraph.</p>
- Inline elements, such as
-
-
Using the
<div>Tag for Layout:- The
<div>tag is often used to create the structure and layout of a webpage, by dividing the content into different sections. - Example of using
<div>to create sections:<div class="header">Header Content</div>
<div class="main-content">Main Content</div>
<div class="footer">Footer Content</div> - Each
<div>can be styled separately using CSS to control its size, position, background, and more.
- The
-
Styling the
<div>Tag with CSS:- Explain how to style a
<div>element using CSS, including properties likewidth,height,margin,padding,background-color, andborder. - Example:
.container {
width: 80%;
margin: 0 auto;
padding: 20px;
background-color: #f0f0f0;
}<div class="container">
<p>This content is inside a styled div.</p>
</div>
- Explain how to style a
-
Creating Inline
<div>Elements:- While the
<div>is a block-level element by default, you can change its display property to make it behave like an inline element using CSS. - Example of changing a
<div>to inline:.inline-div {
display: inline;
padding: 10px;
background-color: #ddd;
}<p>
<div class="inline-div">This is an inline div</div>
<div class="inline-div">Another inline div</div>
</p>
- While the
-
When to Use
<div>vs.<span>:- Use
<div>when you need to group block-level elements or need a block-level container. - Use
<span>when you need to style a specific portion of inline content without breaking the flow of the text.
- Use
-
Common Use Cases for the
<div>Tag:- Layout: Dividing the page into header, footer, sidebar, and content sections.
- Styling: Applying styles to a group of elements collectively.
- JavaScript Targeting: Using
<div>as a container to manipulate content with JavaScript.
-
Examples of
<div>in Action:- Provide examples of how
<div>can be used to structure a simple webpage layout, organize content within a grid, or wrap elements for consistent styling.
- Provide examples of how
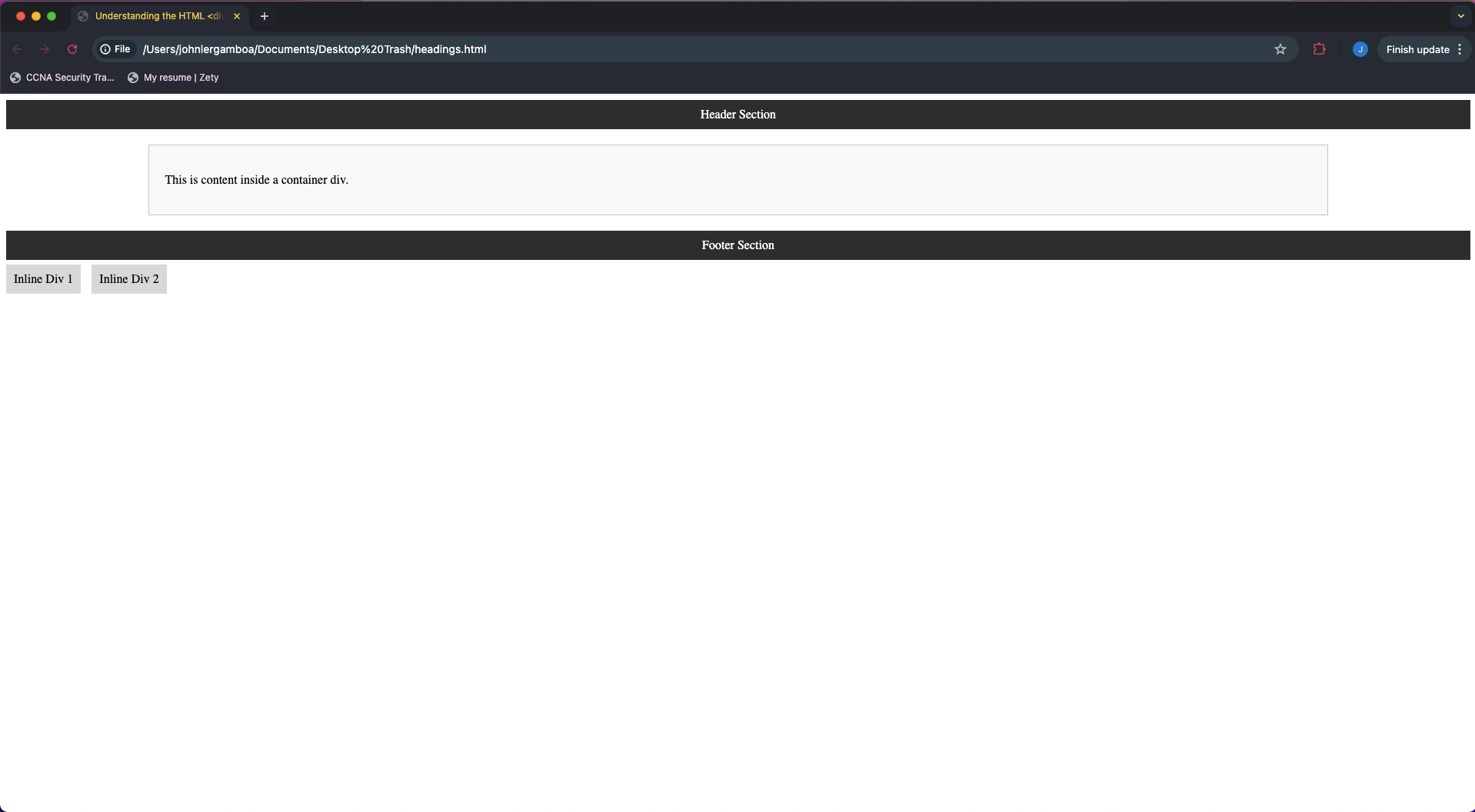
Example Structure:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Understanding the HTML <div> Tag</title>
<style>
.container {
width: 80%;
margin: 0 auto;
background-color: #f9f9f9;
padding: 20px;
border: 1px solid #ccc;
}
.inline-div {
display: inline;
padding: 10px;
background-color: #ddd;
margin-right: 10px;
}
.header, .footer {
background-color: #333;
color: white;
padding: 10px;
text-align: center;
}
.main-content {
background-color: #fff;
padding: 20px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!-- Block-level divs for layout -->
<div class="header">Header Section</div>
<div class="main-content">
<div class="container">
<p>This is content inside a container div.</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="footer">Footer Section</div>
<!-- Inline divs -->
<p>
<div class="inline-div">Inline Div 1</div>
<div class="inline-div">Inline Div 2</div>
</p>
</body>
</html>
Output:
Summary
This topic will help students understand the role of the <div> tag in HTML, including how to use it for structuring content and creating layouts. They’ll also learn the difference between block-level and inline elements, and how to use CSS to control the appearance and behavior of <div> elements.